In this module we’re going to discuss ways to make your app feel and act native. Much of the tips included here are built into Framework7 so you will not need to implement them in this particular app but it’s important to be aware of them when building hybrid apps.
Remove tap highlight
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0);
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent;
Disable user selections on actionable elements (for instance a select on a long tap)
Fix with:
-webkit-user-select: none;
Use the following <meta> tag in your index.html for Microsoft platform support:
<meta name="msapplication-tap-highlight" content="no">
Keep
-webkit-user-select: text;for text input fields or you won’t be able to edit your text.
Remove the glossy appearance from controls on iOS (gives flat design look)
Fix it with:
-webkit-appearance: none;
Disable touch callout (default callout that displays when you hold down on a link)
-webkit-touch-callout: none
See this article:Touch callout disabled
Use Native Scrolling - if the UI framework you’re using doesn’t have this set on the classes you’re using for your containers you should set it.
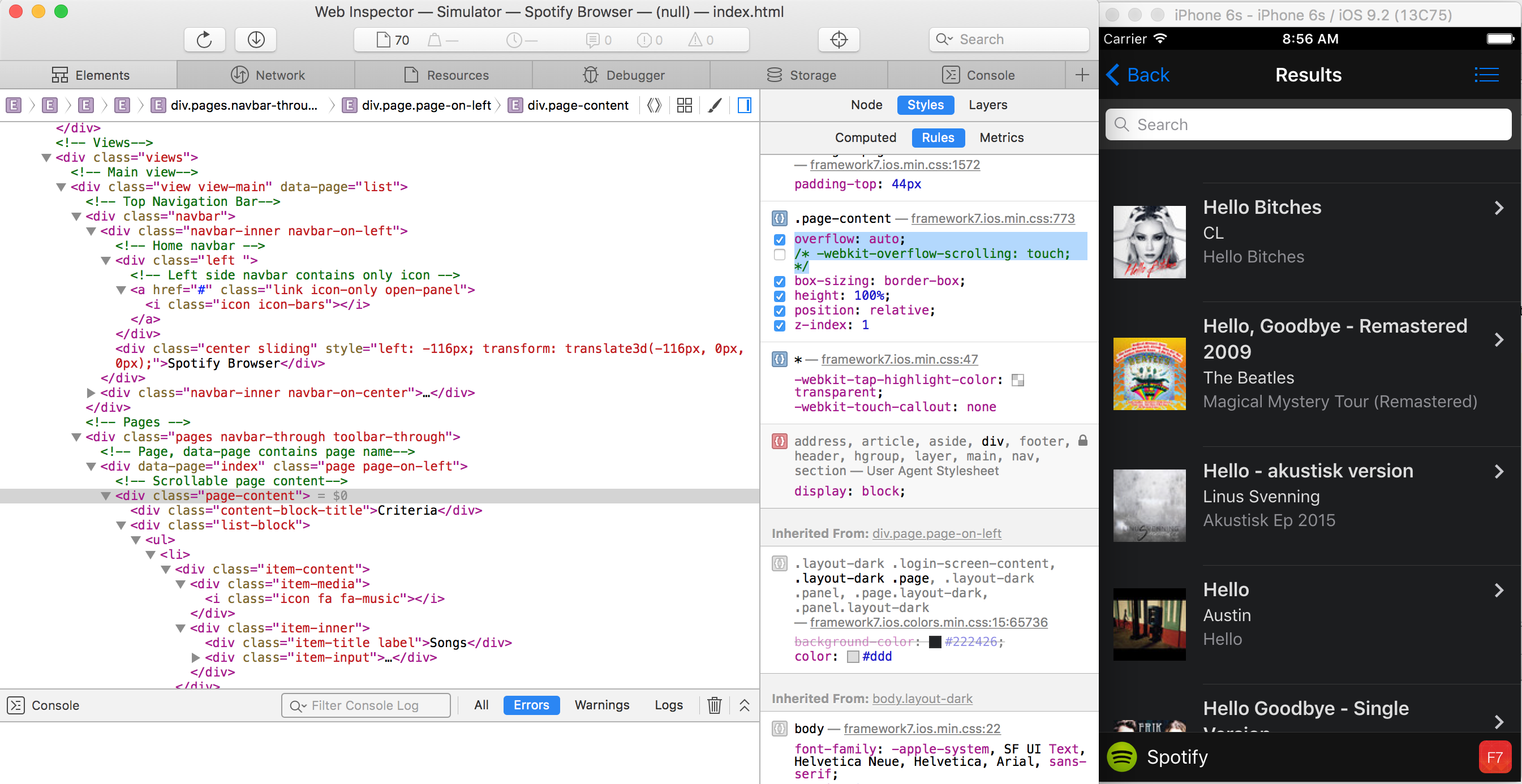
-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch;
On Android 4+ every scrollable container has momentum scrolling.
Use System Fonts
iOS: font-family: 'Helvetica Neue', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
Android: font-family: 'RobotoRegular', 'Droid Sans', sans-serif;
Windows Phone: font-family: 'Segoe UI', Segoe, Tahoma, Geneva, sans-serif;
All of the tips in the above list are already built into Framework7 but important to understand when building hybrid apps.
If you’re running an app through the CLI on a native simulator or device (outside of PhoneGap Developer), you can test out some of these CSS tricks using the Safari Developer tools while remote debugging on your iOS device or the Chrome Developer tools remote debugging your Android device.
See module 9 for remote debugging details
Open up to inspect and modify some of the CSS properties applied from the Framework7 CSS.
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: green;. Then try clicking on one of the external links at the bottom of the main screen.-webkit-touch-callout: none; or change it to another value. Then hold down (long tap) on a link.-webkit-appearance: none;-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch; property in the .page-content definition and notice the
impact on the scrolling feel.-webkit-user-select: none; to the .body` definition in the CSS and try it again to see what happens.Serve properly sized images for all different resolutions. Resolution-independent images (SVG) are a great option and scale well.
Use Hardware Accelerated animations and view transitions (trick to force them to use the GPU - faster than CPU)
.page-on-left {
opacity: .9;
-webkit-transform: translate3d(-20%, 0, 0);
transform: translate3d(-20%, 0, 0)
}
.page-on-center .swipeback-page-shadow {
opacity: 1
}
.page-on-right {
-webkit-transform: translate3d(100%, 0, 0);
transform: translate3d(100%, 0, 0)
}
The Native Transitions Plugin is a Cordova plugin to help increase the speed of your transitions. The plugin immediately grabs a screenshot of your webview (making a more lightweight view), then waits for the new content to load, and then performs the transition by animating out the screenshot and in the new view.
Lazy load images and virtual lists (delay loading of images while outside of viewport until user scrolls to them)
HTML Caching (try to load pages from memory first)
Add the plugin to use the super fast WKWebView on iOS - guide here